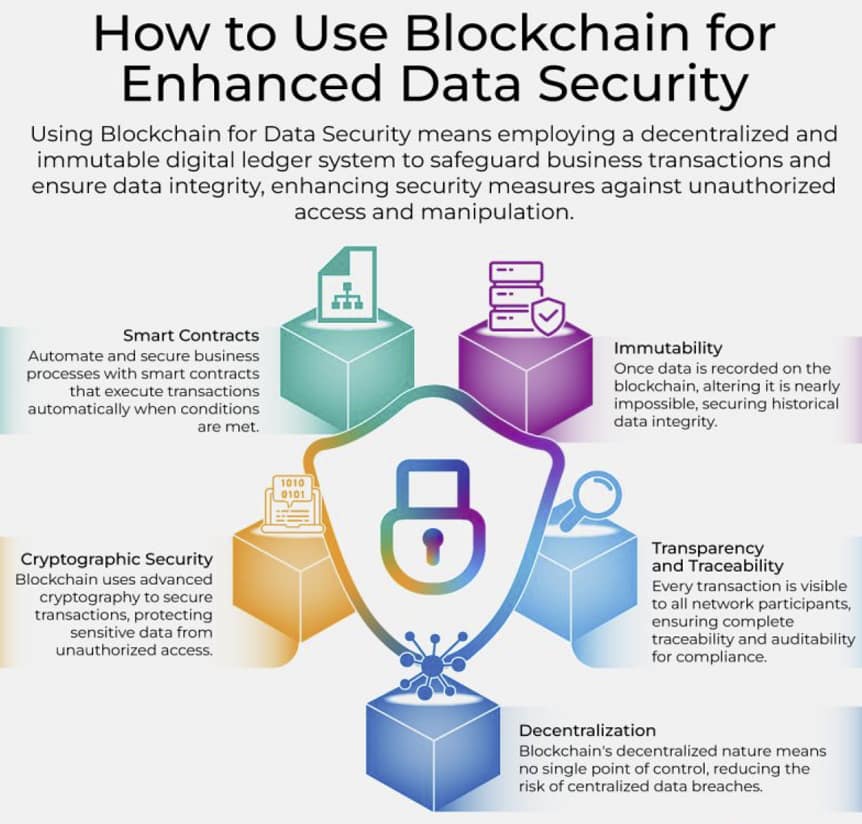
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and distributed ledger system that is inherently secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant. It provides an innovative approach to data security by ensuring the integrity, availability, and non-repudiation of data, making it particularly valuable in safeguarding business transactions and preventing unauthorized access and manipulation.
How Blockchain Enhances Data Security:
- Decentralization and Distributed Ledger:
- Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes, each maintaining a copy of the entire ledger. This eliminates the single point of failure typically associated with centralized databases, making it more resilient against attacks.
- The distributed nature ensures that data is consistently replicated across all nodes, making unauthorized data modification extremely difficult.
2. Immutability of Data:
- Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to alter or delete. Each block is linked to the previous block via a cryptographic hash, creating a chain of blocks that are securely bound together.
- Any attempt to modify a block would require altering all subsequent blocks, which is computationally infeasible in a large, well-distributed blockchain network.
3. Cryptographic Security:
- Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Each transaction is digitally signed using the sender’s private key, ensuring authenticity and non-repudiation.
- The use of public-key cryptography ensures that only authorized parties can access or alter the data, adding an additional layer of security.
4. Consensus Mechanisms:
- Blockchain relies on consensus algorithms (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake) to validate and confirm transactions. These mechanisms ensure that only legitimate transactions are added to the blockchain, preventing fraudulent activities.
- The consensus process requires agreement from the majority of nodes, making it difficult for a malicious actor to tamper with the data.
5. Transparency and Traceability:
- All transactions on a blockchain are transparent and traceable. This transparency allows for real-time auditing and monitoring, which is crucial in identifying and mitigating security threats.
- The traceability ensures that every action on the blockchain is recorded, providing a complete audit trail that can be used for forensic analysis.
How a CISO Can Use Blockchain for Enhanced Data Security:
- Securing Business Transactions:
- Implement blockchain-based systems to secure and verify business transactions. For example, smart contracts can be used to automate and enforce the terms of agreements, reducing the risk of human error or malicious manipulation.
- Use blockchain to maintain a tamper-proof record of transactions, ensuring that all parties involved can trust the integrity of the data.
2. Ensuring Data Integrity:
- Utilize blockchain to store critical data, such as intellectual property, financial records, and customer data, ensuring that this data cannot be altered or deleted without detection.
- Implement hashing techniques to store only the hashes of large data sets on the blockchain, ensuring the integrity of the data while keeping the blockchain efficient.
3. Enhancing Access Control:
- Use blockchain for decentralized identity management systems, where users have control over their own identity data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Implement blockchain-based access control lists (ACLs) to manage permissions in a transparent and immutable manner, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
4. Auditing and Compliance:
- Leverage blockchain’s transparency and immutability for auditing purposes. Blockchain provides a clear and verifiable audit trail, ensuring that all transactions and data accesses are accounted for.
- Use blockchain to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements by providing regulators with access to an immutable and transparent ledger.
5. Supply Chain Security:
- Implement blockchain to secure the supply chain by tracking and verifying every step in the process, from raw materials to finished products. This ensures that all components are authentic and have not been tampered with.
- Use blockchain to ensure the provenance of goods, preventing counterfeiting and ensuring that only legitimate products enter the market.
6. Disaster Recovery and Data Availability:
- Utilize blockchain’s distributed nature as part of the organization’s disaster recovery strategy. In the event of a cyberattack or system failure, the decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that data remains available and intact across multiple nodes.
- Implement blockchain to replicate critical data across geographically dispersed nodes, ensuring resilience against localized failures or attacks.
7. Collaboration and Information Sharing:
- Use blockchain to facilitate secure and transparent collaboration between different departments or organizations. Blockchain ensures that all parties have access to the same verified data, reducing the risk of miscommunication or data discrepancies.
- Implement blockchain-based platforms for sharing threat intelligence securely and anonymously, helping the organization and its partners stay ahead of emerging threats.
By integrating blockchain technology into the organization’s security strategy, a CISO can enhance the protection of business transactions, ensure data integrity, and significantly improve defenses against unauthorized access and manipulation. Blockchain’s inherent security features make it a powerful tool in the ongoing battle to secure digital assets and maintain trust in the digital ecosystem.